This article is my cliff note based on Chris’s blog post at Why are red, yellow, and blue the primary colors in painting but computer screens use red, green, and blue?
The effectiveness of a color system is best measured as the number of different colors that can be created by mixing the primary colors of the system. This set of colors is called the “color gamut” of the system. A color system with a large gamut is more able to effectively represent a wide variety of images containing different colors.
Effective Color System#
The most effective color systems are those that closely match the physical workings of the human eye.
The human eye contains a curved array of light-sensing cells shaped like little cones and rods. Colored light is detected by the cone cells.
The cone cells come in three varieties: red-detecting, green-detecting, and blue-detecting.
They are so named because the red cone cells mostly detect red light, the green cone cells mostly detect green light, and the blue cone cells mostly detect blue light.
Note that even though a red cone cell predominantly detects the color red, it can also detect a little bit of some other colors.
Therefore, even though humans do not have yellow cone cells, we can still see yellow light when it triggers a red cone cell and a green cone cell.
In this way, humans have a built-in color decoding mechanism which enables us to experience millions of colors, although we only have vision cells that predominantly see red, green, and blue.
It should be obvious at this point that the most effective color systems are ones that closely match the human eye, i.e. color systems that mix red, green, and blue light.
Next, we need to know that there are really two main ways to create a light beam or light sources.
We can either create the light directly using light sources or we can reflect white light off of a material that absorbs certain colors.
2 Light Sources#
There are two (2) equally-valid methods for creating color: additive systems and subtractive systems.
- An additive system that creates red, green, and blue light and.
- A subtractive system that creates red, green, and blue light.
Additive System#
For an additive system, light is created directly. This means that the primary colors of the most effective additive color system are simply red, green, and blue (RGB). For example, computer screens, iPods and televisions, contain a grid of little red-, green-, and blue-emitting light sources.
A system that creates light directly is called an “additive” color system since the colors from the different light sources add together to give the final beam of light.
Each image pixel of a computer screen is just a small collection of light sources emitting different colors. If you display an image of a pumpkin on your computer screen, you have not really turned on any orange-emitting light sources in the screen.
Rather, you have turned on tiny red-emitting light sources as well as tiny green-emitting light sources in the screen, and the red and green light add together to make orange.
Subtractive System#
For a subtractive color system, a certain reflected color is obtained by absorbing the opposite color. And the primary colors of the most effective subtractive system are the opposites of red, green, and blue, which happen to be cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY). This is why most printed images contain a grid of little cyan, magenta, and yellow dots of ink. Cyan is the opposite of red and is halfway between green and blue. Magenta is the opposite of green and is halfway between blue and red, and yellow is the opposite of blue and is halfway between red and green.
In contrast to an additive system, color systems that remove colors through absorption are called “subtractive” color systems. They are called this because the final color is achieved by starting with white light (which contains all colors) and then subtracting away certain colors, leaving other colors.
Examples of subtractive color systems are paints, pigments, and inks. An orange pumpkin that you see printed in a newspaper is not necessarily created by spraying orange ink on the paper.
Rather, yellow ink and magenta ink are sprayed onto the paper. The yellow ink absorbs blue light and a little green and red from the white light beam, while the magenta ink absorbs green light and a little blue and red, leaving only orange to be reflected back.
Human Eyes#
The color system that best matches the human eye is the red-green-blue color system.
For additive color systems like computer screens, the primary colors of this type of system are red, green, and blue. For subtractive color systems like inks, the primary colors of this type of system are the opposites of red, green, and blue, which are cyan, magenta, and yellow.
The red-yellow-blue painting color system is effectively a corruption of the cyan-magenta-yellow system, since cyan is close to blue and magenta is close to red.
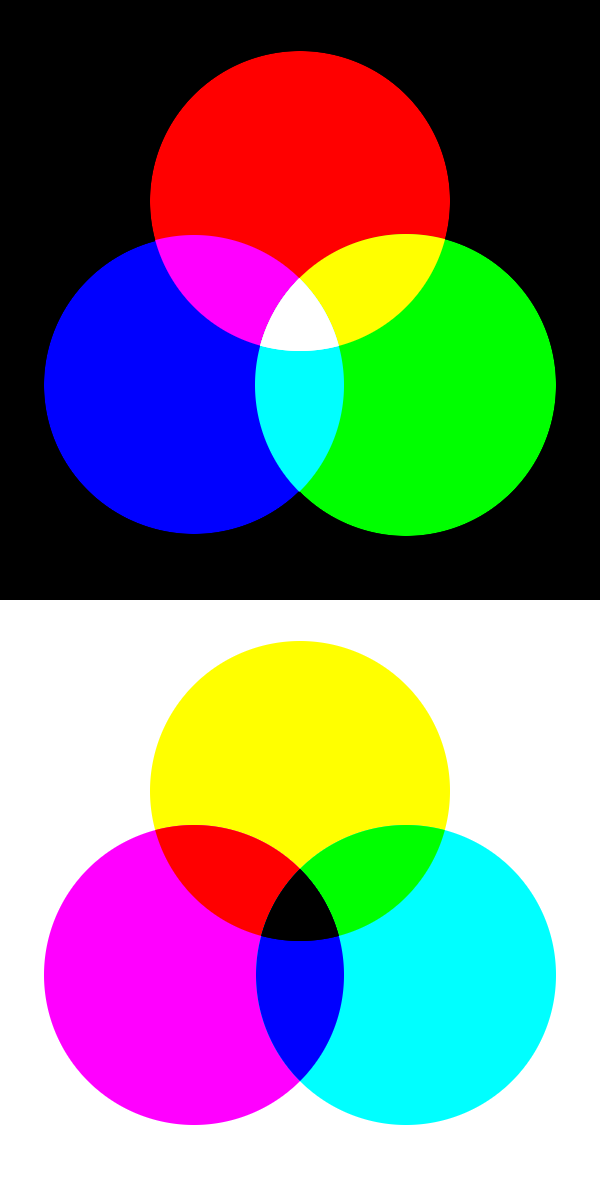
See, usually additive colors/RGB are shown on black-background. (so that it absord and not relecting the colors) And subtractive colors/CYM are shown on a white-background.
